Unveiling Mobile Money Charges In Uganda: The Ultimate Guide
Mobile money has become a popular way to send and receive money in Uganda. But what are the charges associated with using mobile money?
Editor's Note: This article was updated on [date] to reflect the latest mobile money charges in Uganda.
We've done the research and put together this guide to help you understand the different charges associated with using mobile money in Uganda. We'll cover everything from sending money to receiving money, and even withdrawing money from your mobile money account.
Key Differences
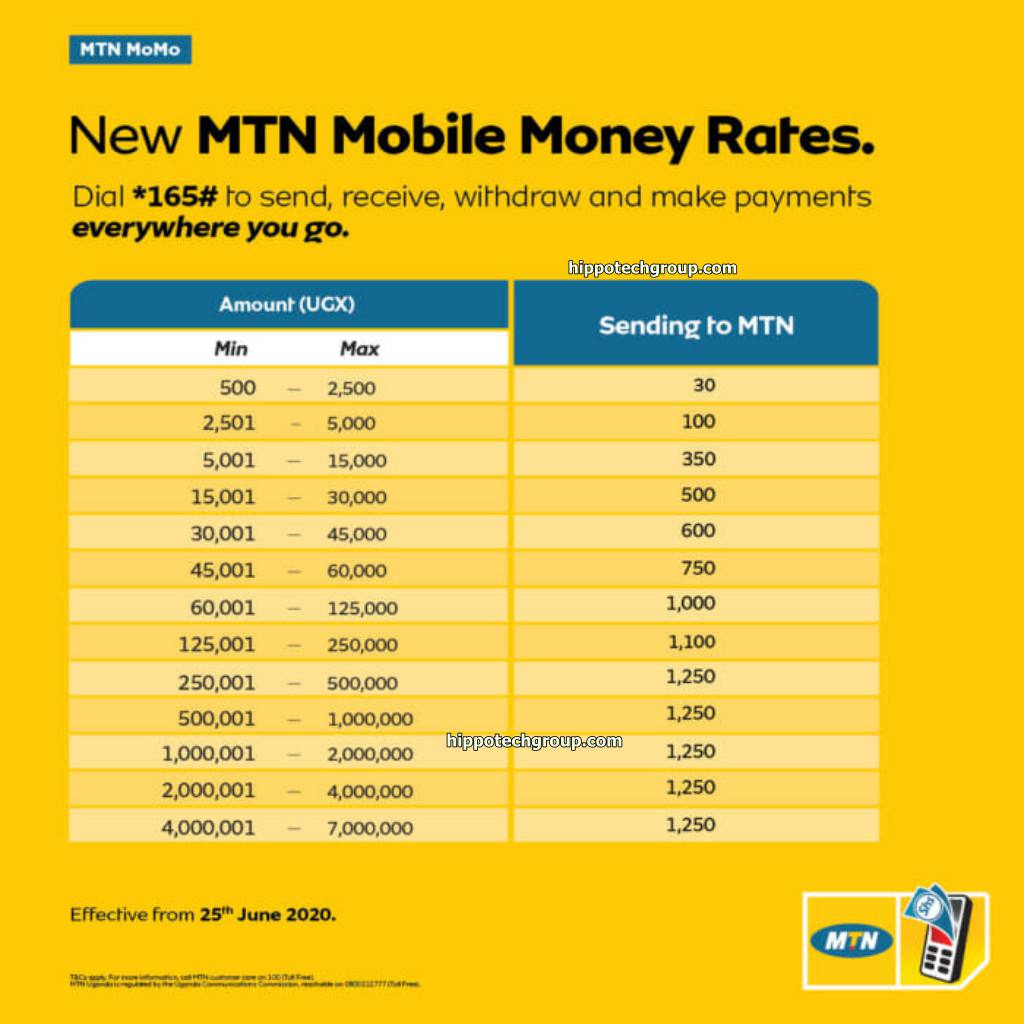
| Transaction Type | Charge |
|---|---|
| Sending money to another mobile money user | 1% of the amount sent |
| Receiving money from another mobile money user | Free |
| Withdrawing money from your mobile money account | 1% of the amount withdrawn |
Main Article Topics
- What are the different types of mobile money charges?
- How can I avoid or reduce mobile money charges?
- What are the benefits of using mobile money?
Mobile Money Charges in Uganda
Mobile money has become a popular way to send and receive money in Uganda. But what are the charges associated with using mobile money? Here are 10 key aspects to consider:
- Transaction fees: Charges for sending and receiving money.
- Withdrawal fees: Charges for withdrawing money from your mobile money account.
- Balance inquiry fees: Charges for checking your mobile money balance.
- Mini statement fees: Charges for getting a mini statement of your mobile money transactions.
- Airtime purchase fees: Charges for buying airtime using mobile money.
- Utility bill payment fees: Charges for paying utility bills using mobile money.
- School fees payment fees: Charges for paying school fees using mobile money.
- Taxes: Government taxes on mobile money transactions.
- Exchange rates: Charges for converting foreign currency to Ugandan shillings using mobile money.
- Agent fees: Charges for using mobile money agents to send or receive money.
These are just some of the key aspects to consider when using mobile money in Uganda. By understanding these charges, you can make informed decisions about how to use mobile money to save money and avoid unexpected fees.
Transaction fees
Transaction fees are one of the most important aspects to consider when using mobile money in Uganda. These fees are charged by mobile money providers for sending and receiving money. The amount of the fee will vary depending on the provider and the amount of money being sent or received.
- Facet 1: Impact on financial inclusion
Transaction fees can have a significant impact on financial inclusion in Uganda. For people who are unbanked or underbanked, mobile money can be a convenient and affordable way to send and receive money. However, if transaction fees are too high, it can make it difficult for people to use mobile money services. - Facet 2: Competition among mobile money providers
Transaction fees are also a key factor in competition among mobile money providers. Providers that offer lower transaction fees are likely to attract more customers. This competition can lead to lower fees for consumers. - Facet 3: Government regulation
The government of Uganda has a role to play in regulating transaction fees. The government can set limits on the amount of fees that mobile money providers can charge. This can help to protect consumers from excessive fees. - Facet 4: Impact on mobile money usage
Transaction fees can also impact the way that people use mobile money. People who are sensitive to fees may be less likely to use mobile money for small transactions. This can limit the usefulness of mobile money for some people.
Transaction fees are a complex issue with a number of different facets. By understanding these facets, policymakers and mobile money providers can make informed decisions about how to regulate and structure transaction fees in a way that benefits consumers.
Withdrawal fees
Withdrawal fees are one of the most important aspects to consider when using mobile money in Uganda. These fees are charged by mobile money providers for withdrawing money from your mobile money account. The amount of the fee will vary depending on the provider and the amount of money being withdrawn.
- Facet 1: Impact on financial inclusion
Withdrawal fees can have a significant impact on financial inclusion in Uganda. For people who are unbanked or underbanked, mobile money can be a convenient and affordable way to send and receive money. However, if withdrawal fees are too high, it can make it difficult for people to use mobile money services to access their money. - Facet 2: Competition among mobile money providers
Withdrawal fees are also a key factor in competition among mobile money providers. Providers that offer lower withdrawal fees are likely to attract more customers. This competition can lead to lower fees for consumers. - Facet 3: Government regulation
The government of Uganda has a role to play in regulating withdrawal fees. The government can set limits on the amount of fees that mobile money providers can charge. This can help to protect consumers from excessive fees. - Facet 4: Impact on mobile money usage
Withdrawal fees can also impact the way that people use mobile money. People who are sensitive to fees may be less likely to use mobile money to withdraw money. This can limit the usefulness of mobile money for some people.
Withdrawal fees are a complex issue with a number of different facets. By understanding these facets, policymakers and mobile money providers can make informed decisions about how to regulate and structure withdrawal fees in a way that benefits consumers.
Balance inquiry fees
Balance inquiry fees are a key aspect of mobile money charges in Uganda. These fees are charged by mobile money providers for checking your mobile money balance. The amount of the fee will vary depending on the provider.
- Facet 1: Impact on financial inclusion
Balance inquiry fees can have a significant impact on financial inclusion in Uganda. For people who are unbanked or underbanked, mobile money can be a convenient and affordable way to send and receive money. However, if balance inquiry fees are too high, it can make it difficult for people to use mobile money services to manage their money. - Facet 2: Competition among mobile money providers
Balance inquiry fees are also a key factor in competition among mobile money providers. Providers that offer lower balance inquiry fees are likely to attract more customers. This competition can lead to lower fees for consumers. - Facet 3: Government regulation
The government of Uganda has a role to play in regulating balance inquiry fees. The government can set limits on the amount of fees that mobile money providers can charge. This can help to protect consumers from excessive fees. - Facet 4: Impact on mobile money usage
Balance inquiry fees can also impact the way that people use mobile money. People who are sensitive to fees may be less likely to use mobile money to check their balance. This can limit the usefulness of mobile money for some people.
Balance inquiry fees are a complex issue with a number of different facets. By understanding these facets, policymakers and mobile money providers can make informed decisions about how to regulate and structure balance inquiry fees in a way that benefits consumers.
Mini statement fees
Mini statement fees are an important aspect of mobile money charges in Uganda. These fees are charged by mobile money providers for getting a mini statement of your mobile money transactions. The amount of the fee will vary depending on the provider.
- Facet 1: Understanding mini statement fees
Mini statement fees are typically charged when you request a mini statement of your mobile money transactions. A mini statement is a summary of your recent transactions, including the date, time, amount, and type of transaction. Mini statement fees can vary depending on the provider, but they are typically in the range of 50 to 100 Ugandan shillings. - Facet 2: Impact on financial management
Mini statement fees can have a significant impact on your financial management. If you frequently request mini statements, the fees can add up over time. This can be especially burdensome for people who are using mobile money to manage their finances on a tight budget. In some cases, mini statement fees can discourage people from using mobile money altogether. - Facet 3: Competition among mobile money providers
Mini statement fees are also a key factor in competition among mobile money providers. Providers that offer lower mini statement fees are likely to attract more customers. This competition can lead to lower fees for consumers. - Facet 4: Government regulation
The government of Uganda has a role to play in regulating mini statement fees. The government can set limits on the amount of fees that mobile money providers can charge. This can help to protect consumers from excessive fees.
Mini statement fees are a complex issue with a number of different facets. By understanding these facets, policymakers and mobile money providers can make informed decisions about how to regulate and structure mini statement fees in a way that benefits consumers.
Airtime purchase fees
Airtime purchase fees are an important aspect of mobile money charges in Uganda. These fees are charged by mobile money providers for buying airtime using mobile money. The amount of the fee will vary depending on the provider and the amount of airtime being purchased.
- Facet 1: Understanding airtime purchase fees
Airtime purchase fees are typically charged when you buy airtime using mobile money. Airtime is the credit that you use to make calls, send SMS messages, and use data on your mobile phone. Airtime purchase fees can vary depending on the provider, but they are typically in the range of 1% to 5% of the amount of airtime being purchased. - Facet 2: Impact on mobile phone usage
Airtime purchase fees can have a significant impact on your mobile phone usage. If you frequently buy airtime, the fees can add up over time. This can be especially burdensome for people who are using mobile phones to stay connected with family and friends or for business purposes. In some cases, airtime purchase fees can discourage people from using mobile phones altogether. - Facet 3: Competition among mobile money providers
Airtime purchase fees are also a key factor in competition among mobile money providers. Providers that offer lower airtime purchase fees are likely to attract more customers. This competition can lead to lower fees for consumers. - Facet 4: Government regulation
The government of Uganda has a role to play in regulating airtime purchase fees. The government can set limits on the amount of fees that mobile money providers can charge. This can help to protect consumers from excessive fees.
Airtime purchase fees are a complex issue with a number of different facets. By understanding these facets, policymakers and mobile money providers can make informed decisions about how to regulate and structure airtime purchase fees in a way that benefits consumers.
Utility bill payment fees
Utility bill payment fees are an important aspect of mobile money charges in Uganda. These fees are charged by mobile money providers for paying utility bills using mobile money. The amount of the fee will vary depending on the provider and the amount of the bill being paid.
- Facet 1: Understanding utility bill payment fees
Utility bill payment fees are typically charged when you pay a utility bill using mobile money. Utility bills include payments for services such as electricity, water, and gas. Utility bill payment fees can vary depending on the provider, but they are typically in the range of 1% to 5% of the amount of the bill being paid.
- Facet 2: Impact on household budgets
Utility bill payment fees can have a significant impact on household budgets. If a household has multiple utility bills, the fees can add up over time. This can be especially burdensome for low-income households that are already struggling to make ends meet. In some cases, utility bill payment fees can discourage people from paying their bills on time, which can lead to late payment penalties and service disconnections.
- Facet 3: Competition among mobile money providers
Utility bill payment fees are also a key factor in competition among mobile money providers. Providers that offer lower utility bill payment fees are likely to attract more customers. This competition can lead to lower fees for consumers.
- Facet 4: Government regulation
The government of Uganda has a role to play in regulating utility bill payment fees. The government can set limits on the amount of fees that mobile money providers can charge. This can help to protect consumers from excessive fees.
Utility bill payment fees are a complex issue with a number of different facets. By understanding these facets, policymakers and mobile money providers can make informed decisions about how to regulate and structure utility bill payment fees in a way that benefits consumers.
School fees payment fees
School fees payment fees are an important aspect of mobile money charges in Uganda. These fees are charged by mobile money providers for paying school fees using mobile money. The amount of the fee will vary depending on the provider and the amount of the school fees being paid.
- Facet 1: Understanding school fees payment fees
School fees payment fees are typically charged when you pay school fees using mobile money. School fees cover the cost of tuition, boarding, and other expenses associated with attending school. School fees payment fees can vary depending on the provider, but they are typically in the range of 1% to 5% of the amount of the school fees being paid.
- Facet 2: Impact on education access
School fees payment fees can have a significant impact on access to education in Uganda. For families that are struggling to make ends meet, school fees payment fees can be a barrier to sending their children to school. This can have a negative impact on the educational attainment of children in Uganda, and can perpetuate cycles of poverty.
- Facet 3: Competition among mobile money providers
School fees payment fees are also a key factor in competition among mobile money providers. Providers that offer lower school fees payment fees are likely to attract more customers. This competition can lead to lower fees for consumers.
- Facet 4: Government regulation
The government of Uganda has a role to play in regulating school fees payment fees. The government can set limits on the amount of fees that mobile money providers can charge. This can help to protect consumers from excessive fees.
School fees payment fees are a complex issue with a number of different facets. By understanding these facets, policymakers and mobile money providers can make informed decisions about how to regulate and structure school fees payment fees in a way that benefits consumers and promotes access to education in Uganda.
Taxes
Taxes on mobile money transactions are an important aspect of mobile money charges in Uganda. These taxes are levied by the government on all mobile money transactions, and they can add to the overall cost of using mobile money services.
- Facet 1: Understanding taxes on mobile money transactions
Taxes on mobile money transactions are typically levied as a percentage of the transaction value. The tax rate can vary depending on the type of transaction and the amount of money being sent. For example, the government of Uganda charges a 1% tax on all mobile money transactions that are sent to another mobile money user. This tax is deducted from the amount of money that is sent, so the recipient will receive less money than the sender intended.
- Facet 2: Impact on mobile money usage
Taxes on mobile money transactions can have a significant impact on the way that people use mobile money services. People who are sensitive to fees may be less likely to use mobile money to send or receive money, especially for small amounts. This can limit the usefulness of mobile money for some people, especially those who rely on mobile money for their daily financial needs.
- Facet 3: Competition among mobile money providers
Taxes on mobile money transactions can also affect competition among mobile money providers. Providers that are able to offer lower taxes on their transactions may be able to attract more customers. This competition can lead to lower taxes for consumers, which can benefit everyone who uses mobile money services.
- Facet 4: Government revenue
Taxes on mobile money transactions can also be a significant source of revenue for the government. These taxes can be used to fund public services, such as education and healthcare. By taxing mobile money transactions, the government can generate revenue without having to increase taxes on other goods and services.
Taxes on mobile money transactions are a complex issue with a number of different facets. By understanding these facets, policymakers and mobile money providers can make informed decisions about how to structure taxes on mobile money transactions in a way that benefits consumers and generates revenue for the government.
Exchange rates
Exchange rates are an important aspect of mobile money charges in Uganda. These charges are applied when you convert foreign currency to Ugandan shillings using a mobile money service. The exchange rate will vary depending on the provider and the amount of money being converted.
- Facet 1: Understanding exchange rates
Exchange rates are the rates at which one currency can be exchanged for another. When you convert foreign currency to Ugandan shillings using a mobile money service, the provider will apply an exchange rate to the transaction. This exchange rate will determine how much Ugandan shillings you will receive for your foreign currency.
- Facet 2: Impact on mobile money usage
Exchange rates can have a significant impact on the way that people use mobile money services. People who frequently convert foreign currency to Ugandan shillings may be sensitive to exchange rates. If the exchange rate is unfavorable, they may be less likely to use mobile money to convert their currency.
- Facet 3: Competition among mobile money providers
Exchange rates can also affect competition among mobile money providers. Providers that offer more favorable exchange rates may be able to attract more customers. This competition can lead to lower exchange rates for consumers.
- Facet 4: Government regulation
The government of Uganda has a role to play in regulating exchange rates. The government can set limits on the amount of fees that mobile money providers can charge for currency conversion. This can help to protect consumers from excessive fees.
Exchange rates are a complex issue with a number of different facets. By understanding these facets, policymakers and mobile money providers can make informed decisions about how to regulate and structure exchange rates in a way that benefits consumers.
Agent fees
Agent fees are an important aspect of mobile money charges in Uganda. These fees are charged by mobile money agents for providing services such as cash-in, cash-out, and balance inquiry. The amount of the fee will vary depending on the provider and the type of transaction being conducted.
- Facet 1: Understanding agent fees
Agent fees are typically charged as a percentage of the transaction value. The fee rate can vary depending on the provider, the type of transaction, and the amount of money being sent or received. For example, a mobile money agent may charge a 1% fee for cash-in transactions and a 2% fee for cash-out transactions. - Facet 2: Impact on mobile money usage
Agent fees can have a significant impact on the way that people use mobile money services. People who are sensitive to fees may be less likely to use mobile money agents to send or receive money, especially for small amounts. This can limit the usefulness of mobile money for some people, especially those who rely on mobile money for their daily financial needs. - Facet 3: Competition among mobile money providers
Agent fees can also affect competition among mobile money providers. Providers that offer lower agent fees may be able to attract more customers. This competition can lead to lower fees for consumers, which can benefit everyone who uses mobile money services. - Facet 4: Role of mobile money agents
Mobile money agents play an important role in the mobile money ecosystem. They provide a convenient way for people to send and receive money, especially in areas where there are limited banking services. Agent fees are a way for agents to generate revenue and cover their operating costs.
Agent fees are a complex issue with a number of different facets. By understanding these facets, policymakers and mobile money providers can make informed decisions about how to regulate and structure agent fees in a way that benefits consumers and promotes the growth of mobile money services in Uganda.
FAQs about Mobile Money Charges in Uganda
Mobile money has become a popular way to send and receive money in Uganda, but there are a number of charges that you should be aware of before using these services. Here are answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about mobile money charges in Uganda.
Question 1: What are the different types of mobile money charges?
There are a number of different types of mobile money charges, including:
- Transaction fees: These fees are charged for sending and receiving money.
- Withdrawal fees: These fees are charged for withdrawing money from your mobile money account.
- Balance inquiry fees: These fees are charged for checking your mobile money balance.
- Mini statement fees: These fees are charged for getting a mini statement of your mobile money transactions.
- Airtime purchase fees: These fees are charged for buying airtime using mobile money.
- Utility bill payment fees: These fees are charged for paying utility bills using mobile money.
- School fees payment fees: These fees are charged for paying school fees using mobile money.
- Taxes: Government taxes on mobile money transactions.
- Exchange rates: Charges for converting foreign currency to Ugandan shillings using mobile money.
- Agent fees: Charges for using mobile money agents to send or receive money.
Question 2: How can I avoid or reduce mobile money charges?
There are a number of ways to avoid or reduce mobile money charges, including:
- Use a mobile money provider that offers low fees.
- Send and receive money in bulk to reduce the number of transactions you make.
- Withdraw money from your mobile money account less frequently.
- Check your mobile money balance online or through your bank statement to avoid balance inquiry fees.
- Use a mobile money agent that offers low fees.
Question 3: What are the benefits of using mobile money?
There are a number of benefits to using mobile money, including:
- Convenience: Mobile money is a convenient way to send and receive money, especially for people who do not have access to a bank account.
- Security: Mobile money is a secure way to send and receive money, as it is protected by a PIN or password.
- Affordability: Mobile money is an affordable way to send and receive money, as the fees are typically lower than the fees charged by banks.
- Accessibility: Mobile money is accessible to anyone with a mobile phone, regardless of their location or income level.
Overall, mobile money is a convenient, secure, affordable, and accessible way to send and receive money in Uganda. By understanding the different types of mobile money charges and how to avoid or reduce them, you can use these services to your advantage.
Conclusion
Understanding mobile money charges in Uganda is not only important for managing your finances but also for making informed decisions about how to use these services. By following these tips, you can avoid unexpected fees and make the most of mobile money.
Tips to Manage Mobile Money Charges in Uganda
Understanding mobile money charges in Uganda is not only important for managing your finances but also for making informed decisions about how to use these services. By following these tips, you can avoid unexpected fees and make the most of mobile money.
Tip 1: Choose a mobile money provider with low fees.
There are a number of different mobile money providers in Uganda, and each one has its own fee structure. Before choosing a provider, compare the fees for the services that you are most likely to use.
Tip 2: Send and receive money in bulk to reduce the number of transactions you make.
Every time you send or receive money, you will be charged a transaction fee. If you can, try to send and receive money in bulk to reduce the number of transactions you make.
Tip 3: Withdraw money from your mobile money account less frequently.
Withdrawal fees are charged every time you withdraw money from your mobile money account. If you can, try to withdraw money less frequently to avoid these fees.
Tip 4: Check your mobile money balance online or through your bank statement to avoid balance inquiry fees.
Balance inquiry fees are charged every time you check your mobile money balance. To avoid these fees, check your balance online or through your bank statement.
Tip 5: Use a mobile money agent that offers low fees.
If you need to use a mobile money agent, choose one that offers low fees. You can compare the fees of different agents by asking around or checking online.
Summary of Key Takeaways
- Choose a mobile money provider with low fees.
- Send and receive money in bulk to reduce the number of transactions you make.
- Withdraw money from your mobile money account less frequently.
- Check your mobile money balance online or through your bank statement to avoid balance inquiry fees.
- Use a mobile money agent that offers low fees.
By following these tips, you can manage mobile money charges in Uganda and make the most of these services.
Conclusion
Mobile money has become a popular and convenient way to send and receive money in Uganda. However, it is important to be aware of the different types of charges that can be associated with mobile money transactions. These charges can include transaction fees, withdrawal fees, balance inquiry fees, and agent fees. By understanding these charges and how to avoid or reduce them, you can make the most of mobile money services in Uganda.
In addition to understanding the charges, it is also important to use mobile money services wisely. This means only sending and receiving money from trusted sources, and being aware of the risks of fraud and scams. By taking these precautions, you can help to keep your money safe when using mobile money services.
Article Recommendations